Weight Reductions with 3D Printing
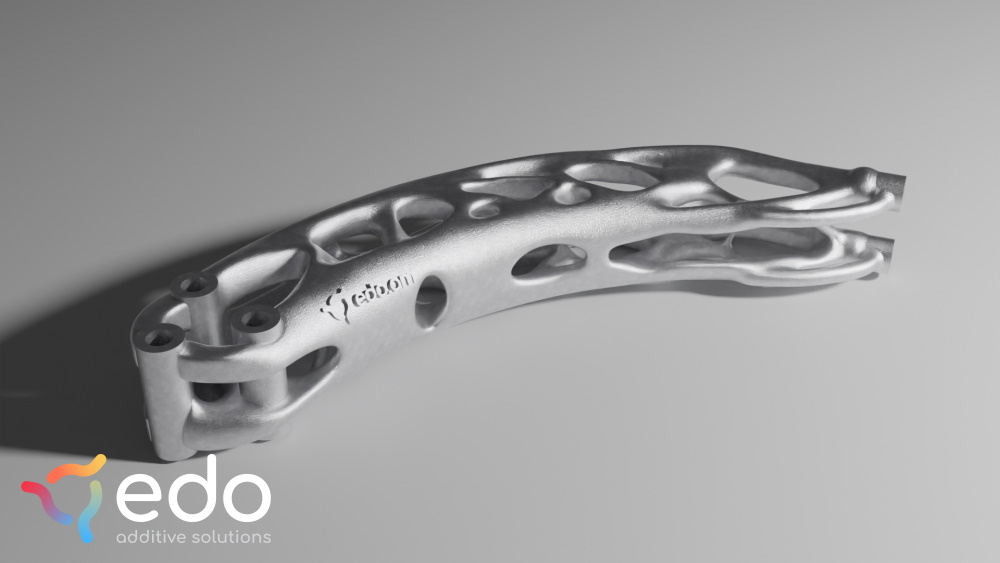

Introduction
In a world where efficiency and sustainability become increasingly important, the significance of weight reduction in manufacturing cannot be overstated. Traditional manufacturing methods often entail excessive material usage, leading to heavier and bulkier end products. However, the advent of 3D printing technology has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape, offering a promising avenue for substantial weight reductions without compromising structural integrity. This article explores the impact of 3D printing in weight reduction strategies across diverse industries and highlights key design approaches that harness its potential.
Why Should You Care?
The allure of weight reduction through 3D printing transcends mere innovation; it directly addresses concerns in modern manufacturing. By significantly trimming down material usage, 3D printing not only optimizes performance, but also production resource utilization. This efficiency translates into real benefits like cost and CO2 savings as well as increased performance.
Benefits of Weight Reduction through 3D Printing
3D printing allows for intricate designs and complex geometries that were previously unattainable with conventional manufacturing methods. By reducing the need for post-processing and minimizing material waste, this technology accelerates production cycles and curtails manufacturing costs.
The lightweight nature of optimized 3D-printed components minimizes the overall weight of end products, leading to reduced fuel consumption during transportation. This weight reduction not only cuts down on CO2 emissions but also translates into substantial cost savings over time for companies like airlines.
Advantages for Diverse Applications
The versatility of 3D printing in weight reduction extends to various industries.
Robot Arms Requiring Swift Movements
Efficient and lightweight components in robot arms are essential for swift and precise movements. 3D printing enables the creation of intricate yet lightweight structures that cater to these demands. It also allows for the use of smaller and cheaper robots for the same application.

A topology optimized robot arm helps to maintain performance even under complex loads
Aerospace Lightweight Components
In aerospace, where every gram matters, 3D printing plays a pivotal role. Each saved gram translates to significant reductions in CO2 emissions and cost savings annually, making it an indispensable technology in this sector.
High-Performance Automotive Applications
The automotive industry benefits immensely from weight reduction through 3D printing. lightweight components enhance vehicle performance, efficiency, and overall sustainability.
Design Strategies for Weight Reduction
Removing Unnecessary Material
A fundamental approach to weight reduction in 3D printing involves rethinking traditional design constraints. Rather than focusing solely on what needs to be added or milled, designers should emphasize what is essential for the intended application, shedding unnecessary bulk without compromising functionality.
Leveraging Lattices and Gyroids
Utilizing lattice structures and gyroids in 3D printing designs enables the creation of lightweight yet robust components. These intricate geometries distribute stress efficiently, offering optimal strength-to-weight ratios.
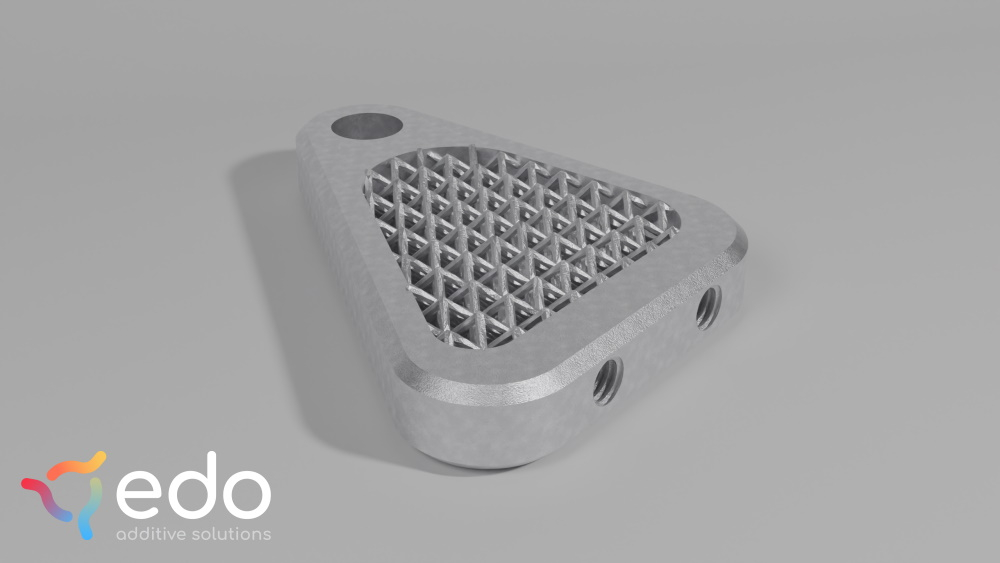
A lattice structure is greatly reducing weight and print time while maintaining stiffness
While these lattices work really well in metal, it can be more challenging in polymer processes like SLS. Thinking even more about the removal of excess powder after printing is crucial. Designers need to account for this during the design phase, as polymer powders are more difficult to remove out of tight spaces than metal powders.
The integration of 3D printing technology presents a compelling avenue for achieving weight reductions in manufacturing across diverse industries. By embracing innovative design strategies and leveraging the inherent advantages of this technology, manufacturers can unlock a future where efficiency, sustainability and performance.
With its potential to revolutionize the production landscape, weight reduction through 3D printing stands as a beacon of progress, offering a transformative path towards a more optimized and sustainable manufacturing ecosystem.
Conclusion
Making parts lighter has many applications and benefits, however doing it in a way that does not hurt the integrity of the part can be challenging. With 3D printing there is a new playground for engineering parts to be lighter, stiffer and more useful. But that often requires a deep understanding of optimisation strategies as shape optimisation, topology optimisation, AI based optimisation, simulation capabilities and a wide understanding of what is feasible from a production and economic standpoint.
Are your parts not using the latest optimization strategies and leave money on the table because your parts are still blocks instead of well optimized structures?
We help you with our research and industry expertise to achieve top performance. Just give us a call or write us here and don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter.
The next releases will cover:
- 3D Printing of Aluminum Alloys
- Lattice Structures and their Applications
- Essential Design Rules for Mass 3D Printing
- 3D Printing In-house vs Contract Manufacturing
- How to Find the Right 3D Printing Process
Subscribe to our newsletter to learn more about additive manufacturing.